Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a sudden blockage of the central retinal artery, a blood vessel that supplies the retina in the eye with blood. This blockage is typically caused by a blood clot or cholesterol deposit in the artery. CRAO can lead to sudden vision loss in one eye and may have serious implications. Some key points about central retinal artery occlusion include:
Symptoms: Symptoms of CRAO include sudden blindness in one eye, sudden and complete blurring of vision in one eye, or a gradual loss of vision over several weeks.
Risk Factors: Risk factors for CRAO include high blood pressure, aging, glaucoma, diabetes, and certain blood conditions that make the blood thicker and stickier. In women, the use of birth control pills has also been associated with an increased risk.
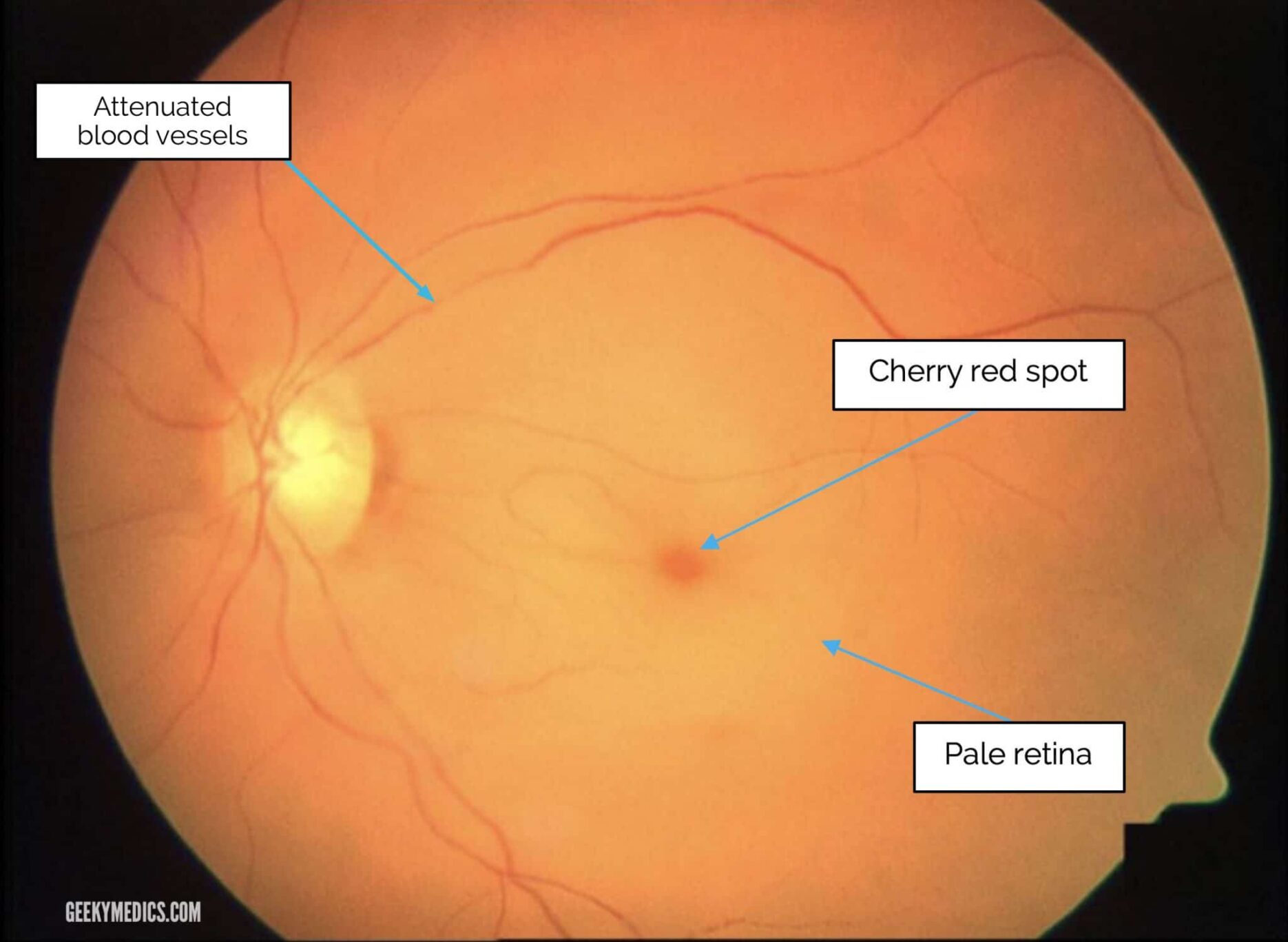
Diagnosis: A healthcare provider can diagnose CRAO through a physical eye examination, eye tests, and blood tests to assess other health factors. Fundoscopy is a common diagnostic test used to examine the retina.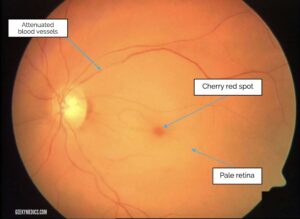 Treatment: Treatment options for CRAO are based on various factors, including the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and clot-busting medications may be considered, but their effectiveness varies among patients and depends on the type of blockage and the timing of treatment.
Treatment: Treatment options for CRAO are based on various factors, including the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and clot-busting medications may be considered, but their effectiveness varies among patients and depends on the type of blockage and the timing of treatment.
Complications: CRAO can lead to partial to permanent loss of vision in the affected eye.
Prevention: While CRAO is often associated with underlying health issues like diabetes and heart problems, preventing heart-related issues and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can be beneficial. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and managing blood sugar levels if you have diabetes.
It’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of CRAO to maximize the chances of preserving vision. However, it’s important to note that treatment outcomes can vary, and there is no guaranteed cure for this condition.




Recent Comments